Thanks for joining me in this DevOps Learning Journey. Let’s explore!
What is Linux?
Linux is an open-source operating system (OS). The Linux OS was developed by Linus Torvalds in 1991, which sprouted as an idea to improve the UNIX OS. He suggested improvements but was rejected by UNIX designers. Therefore, he thought of launching an OS, designed in a way that could be modified by its users. Nowadays, Linux is the fastest-growing OS. It is used from phones to supercomputers by almost all major hardware devices.
-> Linux is a kernel, not OS
-> Linux is not a UNIX derivative it was written from the scratch
-> A Linux distribution is the Linux kernel and a collection of software that together, create an OS
-> Linux distribution means different types of Linux version
-> Secure :
-> Light weight - less memory required
-> Package means Software
-> OS = Kernel + GNU (Collection of software)
- OS = Kernel + software packages
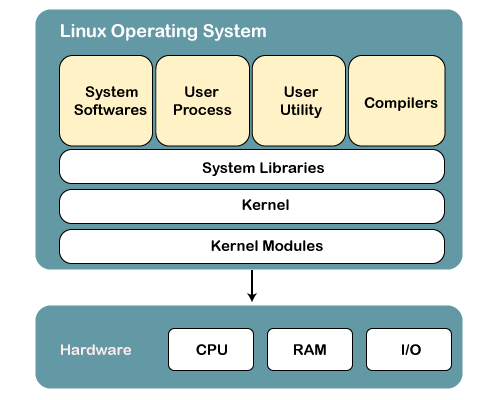
Structure of Linux
Why should we learn Linux?
Free and Open-Source.
Extremely Flexible.
Lightweight Infrastructure.
Great in-build security
End-to-end encryption
Portable Environment
Shell/ Command-line Interface
Automation friendly
What is a “distribution?”
Linux has a number of different versions to suit any type of user. From new users to hard-core users, you’ll find a “flavor” of Linux to match your needs.
Popular Linux distributions include:
LINUX MINT
DEBIAN
UBUNTU
SOLARIS
FEDORA
OPENSUSE
And don’t think the server has been left behind. For this arena, you can turn to:
Red Hat Enterprise Linux
Ubuntu Server
Centos
SUSE Enterprise Linux
Basic Linux commands:-
cd path_to_directory--> change directory to the provided pathcd ..--> chnage directory to one step back.cd ../..--> Change directory to 2 levels back.cd ~or justcd--> change directory to the home directorypwd--> print work directory. Gives the present working directory.whoami→ to know current usernamedate-> to see current date and time with time zoneuptime-> to see host uptimetop--> current running processes with high cpufree -m--> to know current memory and swap usagedf -h--> information about all the file systems human readable formatgrep-> to filter with specific namemkdir-> make directorymkdir -p A/B/C/D/E-> to create a nested directory A/B/C/D/E. The -p switch creates parents’ directories.touch-> make file (with specific extension if specified)ls-> list the sub directories and files avaiable in the present directoryls -l--> list the files and directories in long list format with extra informationls -a--> list all including hidden files and directoryll--> The ll command can be used to list the contents of a directory, the properties of a file, or both.echo-> to print somethingawk-> Scans a file line by line ,Splits each input line into fields, Compares input line/fields to pattern ,Performs action(s) on matched linessudo--> to run any command with root previlages|--> It’s called pipe, used to take one command output and send the output to next command as input&&--> to write multiple commands which all will run together but will give separate output/workrestart/init 6-> to restart the host
File System Hierarchy
root = admin
/ -> Top level root directory and below are sub directories e.x. C:\ drive in win
/root - It is home directory for root user
/home - Home directory for other user
/boot - It’s contains bootable files for linux e.g. initrd - POST - Power on self test
/etc - It contains all the configuration files - e.x. Machine hardware configuration file
/usr - by default software are installed in this directory
/bin (binary) - It contains commands used by all users including root user
/sbin (system binary) - It contains commands used by only root user
/opt - Optional Application software packages e.x. chrome
/dev - Essential device file. Then include terminal devices, usb or any attached to the system - e.x. Printer
How to create a file
cat - cat > f1 - ctrl+d to exit file
touch - touch f1 f2 f3 f4 - create empty file
vi/vim
nano
Cat Command
Create new file - create a single file
Concatenate file - To add more than one file into single file
Copy file - To copy the content of x into y
tac (reverse of cat) - to see the content in bottom to top
E.x.
cat > f1 how are you - > greater then means redirect output
cat f1 - see the output of file
cat > f2 i am good
cat >> f1 thank you - >> two time greater than means add new content with existing f1 file content
cat f1 f2 > f3 -> merge file with f1+f2 and create new file f3 = f3
Touch Command
Main uses - Update timestamp
Create an empty file
Create multiple empty file
Change all timestamp of a file
Update only access time of file, modify time of file
E.x.
stat f1 - all the file details are displayed with access time, modify time and update time
touch f1 - create a empty file
touch f2 f3 f4 - create multiple empty file
touch f2 - change timestamp with current timestamp
stat f2 - check the timestamp details
touch -a f3 - only access time change
touch -m f4 - only modified time change
head f1 - top 10 file line
tail f1 - last 10 file line
more f1 - pages - more allows us to view them as a single file separated by lines
less f1 - one screen at a time - less allows us to switch between them
Time Stamp
Access time - Last time when a file was accessed - e.x. touch -a
Change time - Last time when a file metadata (Property) was changed - e.x.
Update time - Last time when a file was modified - e.x. touch -m
VI - Editor command
Programmer text editor
It can be used to edit all kinds of plain text.
E.x.
vi f5 -> create a file
i - insert to write data
Esc
:wq + enter (W= Save, q = Quit)
:w -> Save file
:wq or :x -> save and quit
:q -> quit
:q! -> force quit, no save
Nano Command
nano f6 -> create file and write data
ctrl+x -> exit
Shift+y -> save data and Press enter to exit
User Command
sudo su -> make a root user - sudo means super user do and su = switch user
$ - normal user sign
# - Root user sign
File Command
How to create hidden file
touch .file1
ls -a -> show hidden file and folder
How to Copy file
- cp source destination - e.x. cp f1 f2
How to cut and paste file
- mv source destination - e.x. mv f1 dir1
How to rename file and directory name
- mv old_name new_name - e.x. mv file1 myfile1
Remove - Delete Command
rmdir : this command is used to remove directory (working only if empty)
- e.x rmdir dir1
rmdir -p : Remove both parent and child directory (p-parent )
- e.x. rmdir -p dir1/dir2
rmdir -pv : Remove all the parent and subdirectory along with verbose
rm -rf : Remove even non-empty file and directory
rm -rp : Remove non-empty directory including parent directory
rm -r : Remove empty directory
Basic Linux Commands
- To view what’s written in a file.
Ans: We can do that by simply using ‘cat’ command :
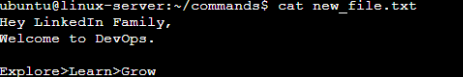
cat file_name.extension
2. To change the access permissions of files.
Ans: For this , command is ‘chmod’ followed by permissions and file name. Here we have first checked which permission is currently present by doing “ll” or “ls -l” .
Now as we can see, execution permission is not present for the specific file, we have given full (r-w-x) permission to both user and user group later on. You can check this link to know more about chmod command and permissions.
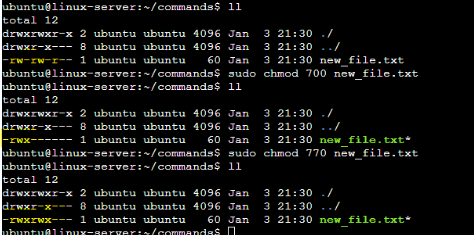
chmod command to give permission
- To check which commands you have run till now.
Ans: We have to run ‘history’ command to check previous commands. Here as I am having nearly 200 commands , I have sorted with last 10 commands using history $n(specific number, for me it’s 10).
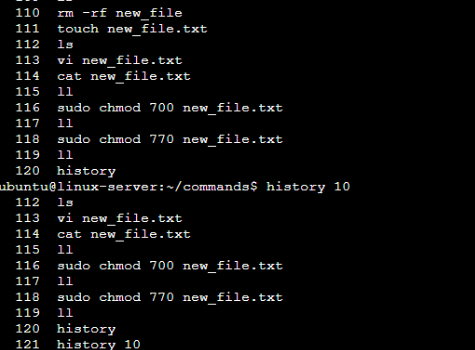
history 10 to get last 10 commands
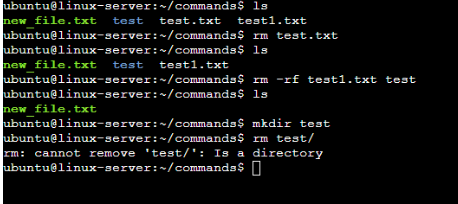
4. To remove a directory/ Folder.
Ans: We have to use rm in case of file; rm –rf in case of directory. Though you can run rm -rf for file also, but it’s not recommended to use this command in production as it will delete everything silently, ignoring all interrupt.
Note: you can’t delete a directory using rm command. You will get error. You have to use rm -rf , so it will also delete all subfolder/file inside that directory. BE CAREFUL.
5. To create a fruits.txt file and to view the content. Add content in devops.txt (One in each line) — Apple, Mango, Banana, Cherry, Kiwi, Orange, Guava.
Ans: You can use vi or vim or nano text editor as per your OS flavor. Here I have used vim.
For VI/VIM :- type vim filename>press “i” to go to insert mode> add your content> press ESC> type “:”> type {wq or wq!} if you want to save your work and quit else {q!} to quit without saving.
For nano:- type nano filename>add your content>press ctrl+x > Capital Y(for yes to save) > ENTER.
Now you can use cat command to see the content!
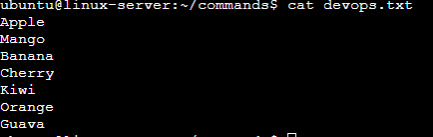
Checking file content after editing with text editor
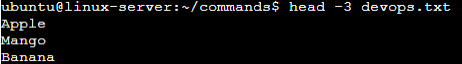
6. To Show only top three fruits from the file.
Ans: “head” [space] -number’ (of items you want to see) [space] ‘filename.txt’ , this command will help you to achieve your result.
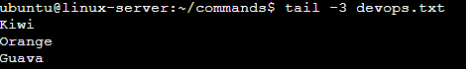
7. To Show only bottom three fruits from the file.
Ans: As you remember, we have used “head” to see top items. To see from bottom, we do use “tail” command. Syntax is same as “head” command.
8. To create another file Colors.txt and to view the content. Add content in Colors.txt (One in each line) — Red, Pink, White, Black, Blue, Orange, Purple, Grey.
Ans: Refer number-5. Same process followed.
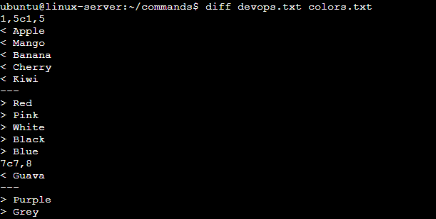
9. To find the difference between fruits.txt and Colors.txt file.
Ans: We use “diff” command to know difference between multiple files. Syntax is simple ; diff ‘file1.txt’ file2.txt’
What is Kernel?
The Linux® kernel is the main component of a Linux operating system (OS) and is the core interface between a computer’s hardware and its processes. It exists within the OS and controls all the major functions of the hardware, whether it’s a phone, laptop, server, or any other kind of computer.
What is Shell?
A shell is a special user program that provides an interface for the user to use operating system services. Shell accepts human-readable commands from users and converts them into something which the kernel can understand. It is a command language interpreter that executes commands read from input devices such as keyboards or from files. The shell gets started when the user logs in or starts the terminal.
What is Linux Shell Scripting for DevOps?
Shell Scripting is a program to write a series of commands for the shell to execute. Shell is a command-line interpreter and Shell script is nothing but a list of commands executed by the shell. It can combine lengthy and repetitive sequences of commands into a single and simple script that can be stored and executed anytime which, reduces programming efforts.
What is
#!/bin/bash?
#!/bin/bash is a shebang line used in script files to set bash, present in the ‘/bin’ directory, as the default shell for executing commands present in the file. “#!” is a shebang in the character sequence consisting of the character’s number sign and exclamation mark ( #!) at the beginning of a script. We must specify this at the beginning of any shell script to let the script know, under which shell it’s being run.
Can we write
#!/bin/shas well?
#!/bin/sh: It is used to execute the file using sh, which is a Bourne shell, or a compatible shell.
Just like that, we have #!/bin/csh. It is used to execute the file using csh, the C shell, or a compatible shell.
-: Basic Linux Commands :-
Write a Shell Script which prints
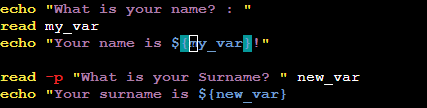
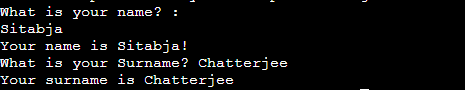
Write a Shell Script to take user input, input from arguments, and print the variables.
See the output difference of both the commands.
1st one output is showing in next line, whereas in 2nd one,output is showing in
same line itself.
Also for variables, in 2nd example , we took input and variable in same line.
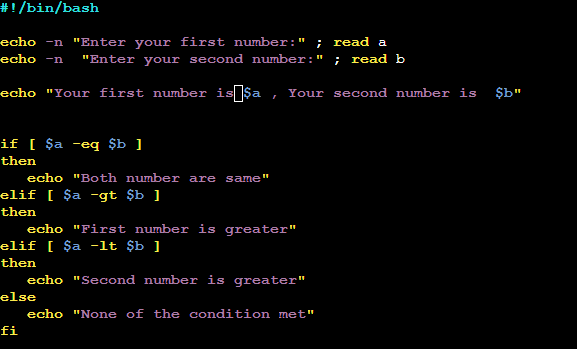
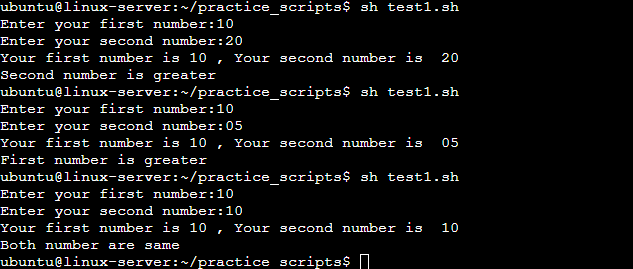
- Write an Example of If else in Shell Scripting by comparing two numbers.
Linux daily uses command:
sudo su - make current user to root user
hostname, hostname -i : current working machine ip
ifconfig
cat /etc/os-release
yum install httpd (yum - package - yellowdog updater modified - by default installed)
yum remove httpd (httpd = apache software, d =daemon)
yum update httpd
service httpd start
service httpd status
chkconfig httpd on - (When you open laptop automatically httpd started in backend)
chkconfig httd off
which - find location or find software - e.x. which tree
Whoami - Who are you?
echo - Print Message - also use to create a file [echo ‘welcome’ >> filez, if you write command ‘echo > filez’ then filez lost the existing data and empty the file
yum list installed - list all the installed packages or software in your system
grep : Search the data - e.x. grep root /etc/passwd
pwd - print working directory
sort - sort by alphabetical order in file name - e.x. cmd = sort file1
Ctrl + l -> Clear window terminal shortcut
tree : tree command get output in drawing format with directory and folder structure same as ls command
useradd - To create a user - e.x. useradd sag - check with cat /etc/passwd
groupadd - To create a group - e.x. groupadd DevopsAWS - check with cat /etc/group
gpasswd -a/-M : To add user into group, to add multiple user, -a = single user
gpasswd -a sag DevopsAWS
gpasswd -m sag,raj,kal,vijay DevopsAWS (first create a user then after use this cmd)
ln : hard link - backup - automatically take backup for current folder/file
- - e.x. ln file2 backupfile2
- ls -> show the output of above command
ln -s : soft link - shortcut key/icon - e.x. ln -s file1 softfile(you can write any name)
tar : Tar is archiver used to combine multiple files into one
- tar -cvf dirx.tar dirx : c=create, v=verbose, f=forcefully
gzip : Gzip is a compression tool used to reduce the size of a file
- gzip dir.tar
gunzip : e.x gunzip dirx.tar.gz and tar -xvf dirx.tar : unzip and abstract folder
wget : Wget is the non-interactive network downloader : e.x. wget <url>
Access Mode/Permission Command
Access Mode | File | Directory | |
r | 4 | To Display the content | To list the content |
w | 2 | To Modify | To create or remove |
x | 1 | To execute the file | To enter into directory |
E.x. output : drwxr-wr-- 1 root root 16 Nov 2 09:57 f1
d (directory or file ‘-’ ) | rwx | rw (Group) | r _ | 1 | root | root | 16 |
rwx = 4+2+1 = 7
r_w=4+0+1 = 5
r_ _ = 4+0+0= 4
Command
rwx rwx rwx = 7 7 7
- chmod 777 dirx : full permission of dir
E.x. If you change the permission to file the : d r - x wx r _ then command is chmod 5 3 4 dir1
chmod : change the access mode of file/dir
chown : Change the owner of file or dir : chown sag f1 (Replace ‘root’ with ‘sag’ name)
chgrp : change the group of file or dir : chgrp devops f1
Alphabetic ways
owner= u
Group = g
Other = o
\= same permission
+ add permission
- - remove permission
E.x. r_ rwx wx if apply this permission then use below command
- u=r, g=rwx, o=wx file1
Added write permission to owner and not disturb other for below example
E.x. Cmd = chmod u+w f6 (Added permission)
chmod u-w f6 (Remove Permission)
chmod u=x f6 (Replace permission with write to execute)
chmod u+w,g-x f6 (Multiple permission)
Hope this article with help you to start your linux journey !
Thanks for reading !
- Sagar Radadiya

